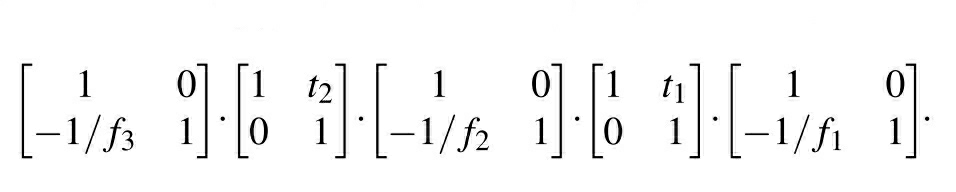Showing posts with label Physics. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Physics. Show all posts
This post specifically pertains to Blackhole energy extraction(Penrose
superradiance).
As known, Black Holes are something which gulps almost everything(except
hypothetical space-like objects). This means Black holes comprise a lot of
energy in different forms. But, is any of that energy useful?. Fortunately, a
long time ago scientists hypothesised two methods(one by Misner in 1968 and
other by Penrose in 1971) which are theoretically possible to extract energy
from a black hole.
To start with, it is important to know what a black hole comprises.
This post specifically pertains to Lamphone technology.
These days privacy is far different from the dictionary meaning. In recent days, losing privacy primarily remembers hacking/compromising any device which contains important or potential information. Moving onto the next step, researchers develop a new method that can be used by the attackers to listen to our conversations just by staring at a light bulb in the room.
To start with, lamphone is a device developed by the researchers which uses small vibrations of the light bulb caused by the sound waves to retrieve audio produced in the room. Basic innards of regular microphones(as described below) are required to know about lamphone.
There is a three-step process which involves three components in a microphone, a device which converts sound waves into an audio signal, they are
Firstly, a diaphragm- which contains a thin piece of material through which sound waves (air pressure fluctuations) pass and create a mechanical motion to the diaphragm.
Not always sci-fi movies heed science, but sometimes scientists heed sci-fi movies too. Well, this commotion is all about cloaking devices used in fictional movies like Harry Potter and Star Trek, which are now an absolute reality. Some of the basic principles of optics are summed up to make things invisible and cloaking possible.
To start from scratch, cloaking devices are something which makes things partially or fully undetected to the electromagnetic spectrum, which entails the visible spectrum. Basic principles of cloaking involve analysis of the well-known Ray transfer matrix/ABCD matrix. By the name itself, it means that these contain matrices (mostly 2×2) which transform the initial/incident rays to the final or emerging rays from an optical device/system as depicted in the picture.
These ABCD matrices are different for different optical lens in different configurations. For a perfect cloaking device, ABCD matrix must be an identity matrix with B differing from 0 to 'L/n' where L is the length of the optical device or system, and n is the refractive index of the surrounding medium. These ABCD matrices should have determinant 1, and other diagonal element(C) must be 0, which means that if we transform object rays which are from infinity, the image rays should also converge at infinity which is termed as afocal.
So to make a cloaking device let us start from one convex lens and refractive index 1 for which the ABCD matrix will be
which is not the one required or satisfied by the matrix for the perfect cloaking device.
Moving onto two lenses the ABCD matrix will be
This also does not satisfy the cloaking matrix
Next with three lenses, the ABCD matrix will be
By condition, setting C as zero, we get the answer which also does not suffice the required condition.
At last, getting onto four lenses, they must be arranged so that the first two must be symmetric to the other two so as to reduce the mathematical burden, which makes the ABCD matrix look like
From this and further calculation on increasing number of lenses, it can be concluded that at least four lenses must be there to make cloaking possible.
On summarising, this picture depicts the whole thing discussed intuitively.
Further developments made use of metamaterials, something that is engineered to have a property that is not found in naturally occurring materials, to build cloaking devices.
REFERENCES/CITATIONS
Choi, Joseph & Howell, John. (2014). Paraxial Ray Optics Cloaking. Optics Express. 22. 10.1364/OE.22.029465.
M. McCall, “Transformation optics and cloaking,” Contemp. Phys. 54, 273–286 (2013).
B. Zhang, “Electrodynamics of transformation-based invisibility cloaking,” Light. Sci. Appl. 1, e32 (2012).
T. Ergin, N. Stenger, P. Brenner, J. B. Pendry, and M. Wegener, “Three-dimensional invisibility cloak at optical
wavelengths,” Science 328, 337–339 (2010).
T. R. Zhai, X. B. Ren, R. K. Zhao, J. Zhou, and D. H. Liu, “An effective broadband optical ’cloak’ without
metamaterials,” Laser Phys. Lett. 10, 066002 (2013).
J. S. Li and J. B. Pendry, “Hiding under the carpet: A new strategy for cloaking,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 203901
(2008).
Until now, a minimum of two independent calculation methods has received two values that are different by about 10% with a deviation that's statistically irreconcilable. The galaxy M106 accustomed measure the distances of more distant galaxies. The universe has been expanding since the massive Bang occurred 13.8 billion years ago – a proposition first made by the Belgian canon and physicist Georges Lemaître (1894-1966), and first demonstrated by Edwin Powell Hubble (1889-1953). The American astronomer discovered in 1929 that each galaxy is pulling removed from us which the foremost distant galaxies are moving the foremost quickly. This means that there was a time within the past when all the galaxies were located at the identical spot, a time that may only correspond to the massive Bang. This research gave rise to the Hubble-Lemaître law, including the constant (H0), which denotes the universe’s rate of expansion. The simplest H0 estimates currently laze 70 (km/s)/Mpc (meaning that the universe is expanding 70 kilometres a second more quickly every 3.26 million light-years). The matter is that there are two conflicting methods of calculation.
 |
| M106 and its anomalous arms used to measure the distance of distant galaxies, Composite of IR (red) and optical light (Credit: NASA, ESA, the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA), and R. Gendler (for the Hubble Heritage Team) |
The first is predicated on the cosmic microwave background: this can be the microwave radiation that comes at us from everywhere, emitted at the time the universe became cold enough for light finally to be ready to circulate freely (about 370,000 years after the massive Bang). Using the precise data supplied by the Planck space mission, and given the actual fact that the universe is homogeneous and isotropic, a worth of 67.4 is obtained for H0 using Einstein’s theory of relativity to run through the scenario. The second calculation method is predicated on the supernovae, which appear sporadically in distant galaxies. These very bright events provide the observer with highly precise distances, an approach that has made it possible to see a worth for H0 of 74. These two values carried on becoming more precise for several years while remaining different from one another. It didn’t take much to spark a scientific controversy and even to arouse the exciting hope that we were perhaps handling a ‘new physics’.To narrow the gap, professor Lombriser entertained the thought that the universe isn't as homogeneous as claimed, a hypothesis which will seem obvious on relatively modest scales. There's little doubt that matter is distributed differently inside a galaxy than outside one. It's tougher, however, to imagine fluctuations within the average density of matter calculated on volumes thousands of times larger than a galaxy.
If we were in a very quite gigantic ‘bubble’, where the density of matter was significantly not up to the known density for the whole universe, it might have consequences on the distances of supernovae and, ultimately, on determining H0. All that might be needed would be for this “Hubble bubble” to be large enough to incorporate the galaxy that is a reference for measuring distances. By establishing a diameter of roughly 250 million light-years for this bubble, we are able to calculate the density of matter inside was 50% not up to for the remainder of the universe, and a replacement value would be obtained for the constant, which might then believe the one obtained using the cosmic microwave background.
AT A GLANCE (Solution to the discrepancy)
The earth, solar system, entire galaxy and therefore the few thousand galaxies closest to us move in a very vast “bubble” that's 250 million light-years in diameter, where the common density of matter is half as large as for the remainder of the universe. This can be the hypothesis to resolve a conundrum that has been splitting the scientific community for a decade: at what speed is that the universe expanding?
This is highly theoretical, and hence no much of experimentation is required to prove and also it's highly difficult to prove it experimentally with this tools and technology equipped in it.
Also, this calculation is predicated on some approximations, and hence there'll be some error, whether or not it's experimentally proved.
Also, no math is kept up here because it gets complicated and difficult for a layman to grasp.